Propagation, the process of growing new plants from a variety of sources such as seeds, bulbs, or cuttings, is a horticultural practice as old as time itself. It's like the plant world's version of cloning, but without the ethical dilemmas and science fiction overtones. So, if you’ve ever fancied yourself as a bit of a green-thumbed Dr. Frankenstein, then this is the guide for you.
The Science of Propagation
Before we dive into the 'how-to', let's take a moment to understand the 'why'. Why do plants allow us to chop off their limbs and grow new ones? Well, it's all thanks to a process called 'totipotency'. This is a fancy term that means every cell in a plant has the potential to regenerate into a whole new plant. It's like every cell is a mini plant blueprint. It's a bit like if every cell in your body had the potential to grow into a whole new you. Terrifying, right?
But don't worry, plants aren't planning world domination (as far as we know). They've just evolved this handy survival mechanism. If a branch falls off, it can potentially grow into a new plant rather than just becoming compost. It's nature's way of making the most out of a bad situation.
Types of Cuttings
There are several types of cuttings you can use to propagate plants. The type you choose will depend on the type of plant you're propagating, the time of year, and how patient you are.
Stem cuttings are the most common type and involve cutting a section of stem from a parent plant and encouraging it to develop its own roots. Leaf cuttings, as the name suggests, involve taking a leaf from a plant and using it to grow a new plant. Root cuttings, on the other hand, involve taking a section of root from a parent plant.
How to Propagate Plants from Cuttings
Now that we've covered the science and types of cuttings, let's get down to the nitty-gritty. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to propagate plants from cuttings.
- Choose the right plant: Not all plants can be propagated from cuttings. Some plants, like succulents and many types of houseplants, are perfect candidates. Others, like most types of trees, are a bit more stubborn.
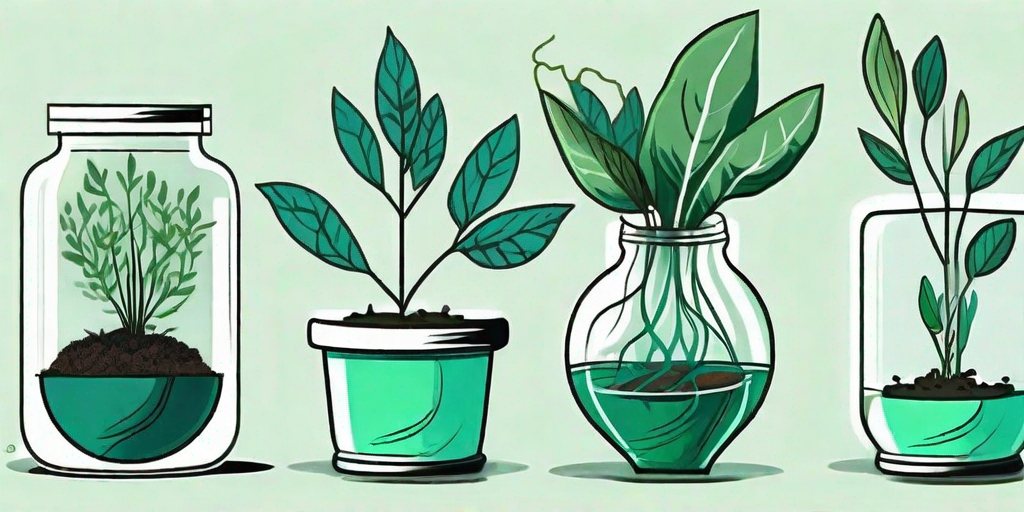
- Take your cutting: Using a clean, sharp knife or pair of scissors, cut a 3-6 inch section of stem, leaf, or root from the parent plant. Make sure to include at least one node (the point where a leaf or branch is or was attached).
- Prepare your cutting: Remove any leaves from the bottom half of the cutting. If you're using a leaf cutting, you can skip this step.
- Root your cutting: Dip the cut end of your cutting in rooting hormone, then stick it in a pot of moist, well-draining soil. Cover the pot with a plastic bag to create a mini greenhouse and keep the cutting moist.
- Wait for roots to develop: This can take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months, depending on the type of plant and cutting. Be patient and keep the soil moist but not waterlogged.
- Transplant your new plant: Once your cutting has developed a healthy root system, you can transplant it to a larger pot or outside, depending on the plant.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Propagation can be a bit tricky, and it's easy to make mistakes. Here are a few common ones to avoid.
- Using dull or dirty cutting tools: This can damage the cutting and introduce disease.
- Not using rooting hormone: While not always necessary, rooting hormone can significantly increase your chances of success.
- Overwatering: Cuttings need to stay moist, but too much water can cause rot.
- Being impatient: Propagation takes time. Don't give up if you don't see roots within the first few weeks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can all plants be propagated from cuttings?
No, not all plants can be propagated from cuttings. Some plants, like many types of trees and shrubs, are best propagated from seeds or grafting.
Do I need to use rooting hormone?
While not always necessary, rooting hormone can significantly increase your chances of success. It's especially helpful for harder-to-root plants.
How long does it take for cuttings to root?
This can vary widely depending on the type of plant and cutting. Some cuttings can root in as little as a few weeks, while others can take several months.
Conclusion
Propagation from cuttings is a fun and rewarding way to expand your plant collection. It's a bit like playing Mother Nature, but without the responsibility of controlling the weather. So why not give it a try? With a bit of patience and care, you could be rooting for your own success in no time.
Remember, every plant is unique, and what works for one might not work for another. But don't be disheartened if your first few attempts don't take root. As with most things in life, practice makes perfect. Or, as we like to say in the horticultural world, 'propagation makes perfect'.